What will I learn?
The bachelor programme Earth, Climate and Technology combines knowledge and skills in Earth sciences, mathematics, physics, and chemistry to better understand how the Earth functions, how we can monitor changes, and how we can responsibly explore the planet for natural resources.
Throughout the programme, you'll explore the Earth system, gaining insights into the processes and properties of the subsurface, surface, water, and atmosphere, along with how these spheres interact. You'll take technical courses in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and geodata science, providing you with a strong foundation for analyzing and understanding Earth's complex systems, as well as designing technical solutions. You will learn how to collect, handle and interpret data, and you will create computer models necessary for measuring and modelling the Earth.
You will be able to apply the knowledge and skills you obtain in this programme to tackle real-world challenges and design innovative technical solutions, such as:
- Exploration and extraction of critical raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and copper: how are these resources currently obtained, and how could we do this more sustainably in the future?
- Designing offshore wind farms and hydrogen storage sites: is the subsurface suitable? What waves and currents must we account for? What are the potential impacts on flora and fauna?
- Storing CO2 in the subsurface: What are the possibilities for subsurface storage? Can we use old gas and oil reservoirs? What is the impact on the surface, and can earthquakes occur?
- How can you use Earth observation technology with satellites to monitor vegetation, water or air quality, or to predict natural disasters and extreme weather?
- Assessing regional climate change impacts: How can we measure and model processes in the atmosphere, sea level rise, and ice cap melting to predict climate change and its consequences?
Mathematics & EC&T
Most high school pupils expect a combination of geography and mathematics when hearing about Earth, Climate and Technology. But in practice, the mathematics provides the basis for the programme.
Read moreDuring the bachelor you follow serveral 'pure' mathematics courses, but mathematics is also an integral part of many other courses. In addition, your math skills will be applied to the subjects ‘Earth and climate’. Think about a dyke for example. When water flows under the structure it decreases the stability of the dyke. Through mathematics you can quantify this water stream and predict how safe the dyke truly is. So by applying the mathematics you can make something visible that you cannot directly see. This way you apply mathematics to the world!
The bachelor programme in Earth, Climate, and Technology takes 3 years. The academic year is divided into two semesters of 20 weeks each. Most courses span an entire semester, with intermediate assessments during the semester. There will be a strong focus on integration and connections between courses. Various teaching methods are used in the courses, including lectures, practicals, workshops, projects and fieldwork.
In addition to the general programme you can take minors (packages of optional subjects), study abroad or do an internship. You will end your bachelor programme with your bachelor end project, in a field of your interest. Once you have your diploma you can transfer to a follow-up Master’s degree programme.
Study schedule
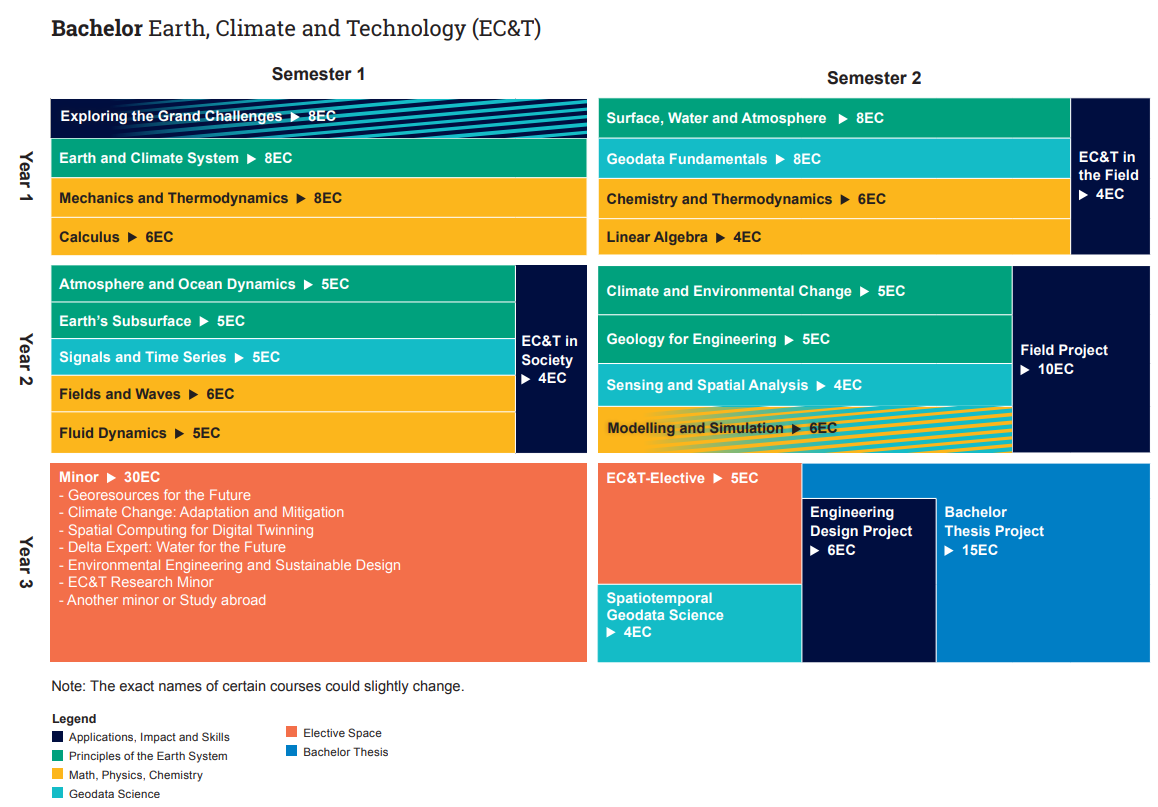
Below, you can see the study schedule of the programme. The colors correspond to the four learning lines; Principles of the Earth System, Geodata Science, Math, Physics and Chemistry and Applications, Impact and Skills.
Principles of the Earth System
In this learning line, you will learn about the Earth system, from the deep subsurface, the surface, the water in and on the Earth, to the atmosphere. You will learn about the processes, the evolution over time from a long time ago to the present, and humanity's influence on the system.
Math, Physics, Chemistry
Mathematics, physics, and chemistry form the backbone that you need in the Earth, Climate, and Technology programme to observe, model, analyze, and interpret relevant phenomena in the Earth system and to design technical solutions.
Geodata Science
In the Geodata Science learning line, you will develop essential skills to extract meaningful information and insights from geodata — data with a spatial component. This involves learning to collect, process, analyze, and interpret geodata to understand the Earth system, manage natural resources, and mitigate geohazards.
Through hands-on experience, you will work with various data types and formats, apply statistical and analytical methods, and account for uncertainty in their analyses. The knowledge gained in this course is foundational for Earth, Climate, and Technology (EC&T) careers, but also widely applicable in any data-driven industry.
Applications, Impact, and Skills
In this learning line, you will apply knowledge and skills in practice. You will collect and analyse real-world data, conduct fieldworks for data collection, and address engineering problems in the field of Earth, Climate, and Technology. You will learn about the need for technical solutions, their impact on society and the environment, and the role of EC&T engineers in designing solutions. Additionally, you will develop important personal, social, and methodological skills such as effective communication, reflection, and research skills. This learning line plays a key role in bringing theoretical knowledge into practice through project work, field data collection, and site visits. At the end of the first and second year you will go on fieldwork in several countries.

Courses
-
In the first semester, you will take the course Exploring the Grand Challenges. The world currently faces challenges in terms of sustaining its population with enough energy and natural resources, while also facing problems such as climate change and pollution. You will investigate the major challenges the world faces and what your future role might be in solving them. In this course, you will also be trained in personal and study skills to help you get off to a good start.
At the end of the first year, you will make a journey along the Maas River from the Ardennes to Rotterdam in the course Earth, Climate and Technology in the Field. During this field course, you will observe, measure, and discuss various processes that you studied in the first year, and examine the links between different components of the Earth system.
-
The introductory course Earth and Climate System focuses on the composition, dynamic processes, and interactions of the various components of the Earth. This gives you a good understanding of the current state of the Earth and climate, and how the Earth and climate might look in the future. You will also explore the history of the Earth and the influence of human activities, now and in the future.
In the second semester, you will delve deeper into surface processes, the water cycle, and their interactions in the course Surface, Water and Atmosphere.
-
In the first semester, as part of the course Exploring the Grand Challenges, you will learn the principles and steps to go from data to interpretation. Data analysis and visualization are taught in combination with programming, using datasets related to the Grand Challenges. In the second semester, you will learn statistical methods for analyzing data and estimating parameters in the course Geodata Fundamentals. In that course, you will also learn about measurement techniques to determine the geometry of the subsurface and Earth's surface and how to process these measurements.
-
In the first semester, you will take the course Calculus, which builds on the mathematics you learned in high school. The course Mechanics and Thermodynamics covers forces, waves, and energy.
In the second semester, you will take the course Linear Algebra, where you will learn to work with matrices and vectors, for example, to solve systems of equations. This is also necessary for the parallel course in the Geodata Science track. In the course Chemistry and Thermodynamics, you will learn about chemical concepts needed for studying things like the chemical composition of rocks or water and air quality.
-
All processes, interventions, and related challenges concerning Earth, Climate, and Technology are embedded in society. The course EC&T in Society focuses on case studies from society, such as energy transition or the impact of technical solutions to mitigate climate change. Interaction with stakeholders and field trips are key components, with critical reflection on ethical aspects, public support, and societal consequences.
Fieldwork is an essential part of our curriculum. In the Field Project, you will work in a team on a project where field data collection abroad plays a central role. During the fieldwork you will study landscapes and geological features, and combine field measurements with technology such as remote sensing with satellites, drones and ground sensors. The fieldwork is part of a group project in which you address a conceptual engineering problem, such as energy or mineral resource extraction.
-
In the first semester, you will learn more about the Earth's subsurface in the course Earth's Subsurface. This includes sediment transport, how rocks form, the properties of rocks, the influence of forces, and plate tectonics. In the same semester, you will also take the course Atmosphere and Ocean Dynamics, where you will learn about the circulation of the atmosphere and oceans and natural variations in these systems.
In the second semester, two courses are on the agenda: Solid Earth System & Engineering and Climate & Environmental Change. You will learn how to apply knowledge of the Earth and climate to Earth, Climate, and Technology applications, such as energy production, resource extraction, and weather and climate prediction.
-
In the first semester you will follow the course Signals and Time Series, which comprises of the components signal processing and time series analysis. Signals can be natural signal in which we are interested, but for instance also electromagnetic radiation, sound, or seismic waves, which we use to measure properties of the Earth with sensors in or on the ground, or from drones or satellites. Properties of the Earth change in time and space, and therefore you learn how to analyse time series as well.
In the second semester you will learn to analyse spatial data in the course on Sensing and Spatial Analysis. In this course you will also learn about measurement techniques to determine geophysical properties.
-
Fluid Dynamics teaches you how fluids, heat, and mass move through different materials in the subsurface, on the surface, or in the air. Fields and Waves covers the physical principles surrounding electricity and magnetism, combined with the necessary mathematics in the form of partial differential equations. Both courses are important for the subjects in the Principles of the Earth System and Geodata Science learning lines in the next semester.
Finally, in the second semester, you will take the course Modelling and Simulation, where you first learn about numerical analysis methods, which you will then need for modeling and simulating processes in the Earth’s system.
-
In the first semester of the third year, you are free to choose a minor. You can take a minor in a completely different discipline, even at another university or abroad. Additionally, we offer several minors that provide a nice broadening of the EC&T programme:
• EC&T Research Minor
• Geo-resources for the Future
• Climate Change: Adaptation and Mitigation
• Spatial Computing for Digital Twinning
• Delta Expert, Water for the Future
• Environmental Engineering and Sustainable Design -
In the second semester, you will take the course Spatiotemporal Geodata Science, which builds on the previous Spatial to Insights courses. At the same time, you will take an EC&T elective, where a specific topic is explored in more depth and/or additional lab skills are trained.
-
The EC&T bachelor’s program lays the foundations for becoming an engineer in this field. Therefore, in this group project, you will learn how to apply all the knowledge and skills you have acquired to solve a problem that requires a technical solution.
-
You finish your degree by writing a thesis. This means that you choose an individual research project in the field of Earth, Climate, and Technology. You will conduct independent research, write a report, and present your findings.